 X-RAY LASER
X-RAY LASER
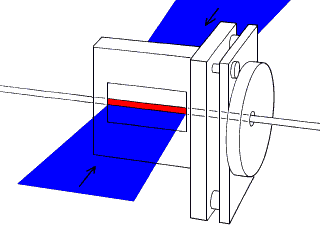
Plasma cylinder (red) created by the impact of a high power pulsed laser (blue).
No mirrors are used, gain is achieved by amplified spontaneous emission and
a beam emerges both in the forward and reverse directions.
(Matthews and Rosen 1985, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory)
The target is made of a thin foil of selenium or other element of high atomic
number deposited on a vinyl substrate to give it rigidity.
The target is irradiated from both sides with a pair of laser pulses from a
high power pump laser whose focus is several hundred times longer
than it is wide.
When it strikes, the foil 'explodes' producing a
plasma consisting of selenium ions stripped of 24 electrons.
The resulting ion has a very high charge, the energy difference of the
outer electrons scales as Z squared (Z=ion charge) this leads to very short
wavelength x-ray transitions.
Since spontaneous decay rates scale as Z to the fourth power, the pump must
supply 1,000 times as much energy and deliver it 10,000 times faster than
an optical laser.
The solution to this problem may be low Z-ions : It may not be necessary to
strip away most of the electrons from a high atomic number element, less drastic
means of x-ray lasing can be achieved by using other x-ray transitions
such as core electrons, which are not shielded by the outer electrons and
feel the full force of the nuclear charge. Also, promising results are
obtained from strong x-ray transitions in core electrons of
atomic microclusters
(research by
Rhodes et al., 1994)
Currently the efficiency of these laser schemes is very low because most are
based on collisional excitation. Much higher efficiency can be achieved
by rapid cooling, leading to three body recombination pumping of a highly
ionized plasma. A hybrid scheme involving contact-cooling and adiabatic
expansion seems to show the most promise.
There is another promising possibility based on
Electromagnetically Induced Transparency (EIT)
to dramatically reduce pump power requirements and obtain highly efficient
Lasing Without Inversion
(also known as phaseonium lasers or phasers).
 PRACTICAL USES OF X-RAY LASERS
PRACTICAL USES OF X-RAY LASERS
The following is a literature survey on the practical engineering
applications of x-ray lasers.
The coherent ultra-short wavelengths would be the only practical way to
manufacturing nanometer scale structures required in the fields of
quantum-electronics and for construction of nanometer sized robots (nanides).
These lasers could also be the only conceivable way to make holograms of
complicated bio-molecules while they are still within a living cell.
And the promise of x-ray lasers for
inertial confinement fusion holds the
promise of unlimited energy for humanity.
a) Nano-Electronics
The circuits required for quantum-electronics are much smaller than
current semiconductor technology.
These devices hold the potential of operating with insignificant dissipation
by using properties of electrons confined to ultra-small cavities of the order
of the wavelength of the electron, taking advantage of wavefunction
quantization. Present day semiconductor VLSI manufacturing technology considers
this quantum wavefunction overlap as an impediment to the 'quasi-classical'
electron-fluid approximation. This outdated approach severely limits the minimum
size of circuit elements before the noise attributed to the 'tunneling' of
electrons from nearby components causes irretrievable signal loss.
Instead of fighting this purely quantum effect, why not take advantage of it by
shifting the emphasis away from the classical conception of an electron-fluid
towards the more 'natural' and powerful quantum concept. Computers based on
nano-electronics would be ultra-dense, hyper-fast and superconducting;
priceless attributes for a world starving for table-top giga-flops and
giga-bits for micro-dollars.
The high spatial resolution of x-ray lasers could be used to shape parts for
nanometer scale robots. These 'nanides' would revolutionize industry and medicine.
In manufacturing technology they could be programmed to
fabricate anything merely by providing them with enough raw materials in a
water based medium. They could build entire personal computers inside something
that looks like a jug of milky liquid ! They could even be programmed to
reproduce themselves in case more are needed. In medicine they could be
programmed to perform nano-surgical repairs anywhere within a living host.
c) Bio-Holography
The coherence and short wavelength of pulsed x-ray lasers could be used to make
holographic snapshots of single bio-molecules within the living cell.
This would allow microbiologists the unprecedented freedom to examine
complicated and fragile organic molecules in their natural environment, while
they still reside within living cells. Under suitable conditions these
molecules could even be 'caught in the act' of important chemical changes
during their normal functioning.
No longer would there be a need for the long a laborious task of isolating,
purifying and growing perfect crystals on the space shuttle etc ...
Most of the larger bio-molecules change their shape when removed from their
natural watery environment, or when they are removed from the cell walls.
During the purification process, vital information about their functioning and
geometrical location and configuration within the living cell is lost.
All these problems are eliminated with x-ray holography. The wavelength
is tuned within the water window where the discontinuous absorption coefficient
allows the x-rays to pass relatively unimpeded compared to other atomic
components of bio-molecules such as carbon. The beam could pass through a
relatively thin layer of water containing the cell. Various cellular
components could be imaged simultaneously in three dimensions during the
holographic snapshot. The cell would most probably be irretrievably damaged
after the exposure, however the vital structural information would be
permanently recorded in the hologram before this occurred.
The only other technology at present which comes close to this 'real-time' capability
is magnetic resonance spectroscopy, however its ability to determine the
exact geometrical structures and positions of bio-molecules within living
cells is somewhat indirect and speculative.
The capability of directly imaging living bio-molecules would allow tremendous
advances to be made in genetics and other areas.
Astronomy
Recent spectra from the ASCA x-ray astronomy mission reveals an x-ray laser
is operating in
quasars PKS 0637-752.
This remarkable evidence provides strong support for the
laser star theory : Strong population inversions
in stellar atmospheres can occur at any wavelength from microwave through optical and
x-ray.
Web References
- Varshni, Y.P. : 1999, Bull.Amer.Phys.Soc., April 1999
Evidence for possible laser action in an x-ray line in the quasar PKS 0637-752
-
X-Ray Lasers : Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (Collisional pumping)
-
Design and applications of laser-plasma x-ray lasers
: An X-Ray Laser Network,
European Commission and 7 laboratories
in France, Germany and United Kingdom.
- Ulf Litzén*,U., Persson,A., Starczewski,T., Steingruber,J., Svanberg,S. Wahlström, C.: 1996,
Division of Atomic Physics, Lund Institute of Technology (LTH) . X-ray laser related investigations
- Colorado State University (CSU) : x-ray laser at 469 Å in a plasma generated by a compact electrical discharge
-
Laser-plasma simulation code: MED103 (useful for computing gain in a recombining plasma x-ray laser)
- Power Viewwing , Planet Science.
- Hively,W.: 1995, Discover Magazine, 'X-ray Dreams' (July)
- Atomic and Molecular Physics team Rhodes,C.K., et al.: 1994,
X-Ray lasers based on Xenon microclusters pumped by photon excitations (see also
McPherson's page at
Univ. of Illinois, Chicago)
- Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen - Discovered x-rays on November 8, 1895
-
X-ray optics and microscopy at Stony Brook
-
X-ray Holography Group -- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
-
Molecular Structure Laboratory - SUNY Stony Brook
-
Hard X-ray microscopy (NASA)
-
National Ignition Facility, NIF (Livermore)
-
X-ray research
-
Gasparyan,P.D.,
Starikov,F.A.,
Starostin,A.N.: 1998, Physics - Uspekhi 41 761
Angular divergence and spatial coherence of x-ray laser radiation
- Fill,E., et al. : 1995, Phys. Rev. E51, 6016. Linearly polarized OFI (Optical Field Ionization) pulse
increases cooling rate of recombination X-Ray lasers. (MPG , Lund)
- Amendt, P., Eder, D. C., & Wilks, S. C.: 1991,
X-ray lasing by optical-field-induced ionization.
Phys. Rev. Lett., 66, 2589-2592.
- Blyth, W. J., Preston, S. G., Offenberger, A. A., Key, M. H., Wark, J. S.,
Najmudin, Z., Modena, A., Djaoui, A., & Dangor, A. E.: 1995,
Plasma temperature in optical field ionization of gases by intense
ultrashort pulses of ultraviolet radiation.
Phys. Rev. Lett., 74, 554-557.
- Burnett, N. H., & Enright, G. D.: 1990,
Population inversion in the recombination of optically-ionized plasmas.
IEEE J. Quant. Elec., 26, 1797-1808.
- Dunne, M., Afshar-Rad, T., Edwards, J., MacKinnon, A. J., Viana, S. M., Willi, O., & Pert, G.: 1994,
Experimental observations of the expansion of an optical-field-induced ionization channel in a gas jet target.
Phys. Rev. Lett., 72, 1024-1027.
- Fill, E. : 1994, X-Ray Lasers (Part II).
Appl. Phys. B, 58, 1.
- Key, M. H.: 1985, X-Ray lasers.
Nature, 316, 314.
- Matthews, D. L., & Rosen, M. D.: 1988, Soft-X-Ray Lasers.
Scientific American, December, 86-91.
- Maxon, S., Estabrook, K. G., Prasad, M. K., Osterheld, A. L., London, R. A., &
Eder, D. C.: 1993,
High gain X-ray lasers at the water window.
Phys. Rev. Lett., 70, 2285-2288.
- Offenberger, A. A., Blyth, W., Dangor, A. E., Djaoui, A., Key, M. H., Najmudin,
Z., & Wark, J. S.: 1993,
Electron temperature of optically ionized gases produced by high intensity 268nm radiation.
Phys. Rev. Lett., 71, 3983-3986.
- Penetrante, B. M., & Bardsley, J. N.: 1991,
Residual energy in plasmas produced by intense subpicosecond lasers.
Phys. Rev. A, 43, 3100.
- Röntgen, W. C.: 1895,
Nature, 53, 274.
- Steyer, M., Schäfer, F. P., Szatmari, S., & Kühnle, G.: 1990,
Feasibility of a laboratory X-ray laser pumped by ultrashort UV laser pulses.
Appl. Phys. B, 50, 265-273.
- Strobel, G. L., Eder, D. C., & Amendt, P.: 1994,
Saturation intensity for ultrashort-pulse X-ray laser schemes.
Appl. Phys. B, 58, 45-50.
- Willi, O., Afshar-Rad, T., Barrow, V., Edwards, J., & Smith, R.: 1989,
Basic physics studies for novel X-ray laser schemes using ultra-short
laser pulses.
Pages 194-199 of: Falcone, R. W., & Kirz, J. (eds),
Short Wavelength Coherent Radiation: Generation and Applications.
New York: AIP.
- Proceedings of the SPIE, (Soc.Photo.opt.Instr.Eng.), 1551 (1992).
- Pert,G.J., Rose,S.J.: 1990, Appl. Phys. B 50, 307
- Matthews,D.L. et al.: 1985,Phys.Rev.Lett., 54, 110.
- Rosen,M.D. et al.: 1985, Phy.Rev.Lett., 54, 106.
- Monot,P. et al. : 1995, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 2953
- Jaeglé,P. et al. & M.H. Key et al., 1996, Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. 151, 1-16.
Collisional X-ray lasers
- Bonnet,L. et al.: 1994, Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. 140, 193
- Groups
- CEA (Commissariat à l'Energie Atomique ) France
- UPS/LSAI, France (recombination lasers)
- MPQ, Germany
- MBI, Germany
- Univ. Essex, United Kingdom
- Univ. York, United Kingdom
- QUB, United Kingdom
- Recombination lasers : H-like (Balmer 3d-2p line, He II) and Li-like (nf-3d line, C IV, N V, O VI), He-like (He I, C III, N IV, O V)
- Osaka, Japan
- American laboratories
- J. Zhang et al. : 1995, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 1335.
H-like Carbon Recombination X-Ray Laser. UK/MPQ groups.
Soon will use the USP UHI (Ultra-High Intensity) laser facilities on H-like Al.
REFERENCES
- Kato,Y., Takuma,H. (eds) : 1998,
X-Ray Lasers : Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on X-Ray Lasers Held in Kyoto,
Japan, 31 August-4 September 1998
Inst of Physics Pub; ISBN: 0750305924
-
Dimauro,L., Murnane,M., L'Huillier A. (eds) : 1997,
Applications of High-Field and Short Wavelength Sources.
Proceedings of the Optical Society of America Conference held March 1997, Santa Fe, New Mexico
Plenum Pub Corp; ISBN: 0306459094
-
Svanberg,S., Wahlstrom,C.-G. (eds): 1996, X-Ray Lasers : Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on X-Ray Lasers Held in
Lund, Sweden, 10-14 June, 1996
Iop Pub/Institute of Physics; ISBN: 0750304065
-
Rocca,J.J., Hagelstein,P.L. (eds): 1995,
Soft X-Ray Lasers and Applications : Proceedings : 10-11 July 1995 San Diego, California (Proceedings of Spie--The International Society for Optical e
Society of Photo-optical Instrumentation Engineers; ISBN: 081941879X
- Eder,D., Matthews,D. (eds) : 1994, X-Ray Lasers,
AIP, New York.
-
1994, High Field Interactions and Short Wavelength Generation : Summaries of Papers Presented at the Topical Meeting ... August 22-25, 1994,
St. Malo, France
Optical Society of America; ISBN: 1557523614
-
1993, Ultrashort wavelength lasers II : 12-13 July 1993, San Diego, California
ISBN: 0819412619
-
Korobkin,V.V., Romanovsky, M.Yu. (eds) : 1992,
Short Wavelength Lasers and Their Applications : Proceedings of International Symposium, Samarkand, Ussr, May 14-18, 1990
Nova Science Publishers, Inc.; ISBN: 1560720204
-
1992, Short Wavelength Lasers and Their Applications
Nova Science Publishers, Inc.; ISBN: 1560720209
-
Fill,E.E. (ed) : 1992, X-Ray Lasers : Proceedings of the 3rd International Colloquium Held at Schliersee, Germany, 18-22 May 1992
Iop Pub/Inst of Physics; ISBN: 0854984151 Lib. Congress Num : TA1707.X28
- Sprangle,P. (ed) : 1991,
Short-Wavelength Radiation Sources : 24-25 July, 1991 San Diego, California (Spie Proceedings, Vol. 1552)
Society of Photo-optical Instrumentation Engineers; ISBN: 0819406805
-
Suckewer,S. (ed) : 1991, Ultrashort Wavelength Lasers : 22-23 July, 1991 (Spie Proceedings, Vol. 1551)
Society of Photo-optical Instrumentation Engineers; ISBN: 0819406791
-
Tallents,G.J, (ed) : 1990, X-Ray Lasers : Proceedings of the 2nd International Colloquium Held at the University of York, 17-21 September 1990
Iop Pub/Inst of Physics; ISBN: 085498044X Lib. Congress Num : TA1707.X27
- Elton,R.C.: 1990, X-Ray Lasers
Academic Press; ISBN: 0122380800 Lib. Congress Num : TA1707.E37
-
Falcone,R.W., Kirz,J. (ed) : 1989,
Osa Proceedings on Short Wavelength Coherent Radiation : Generation and Applications
Optical Society of America; ISBN: 1557520534
- Yamanaka, C. (ed) : 1988,
Short-Wavelength Lasers and Their Applications : Proceedings of an International Symposium (Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol 30)
Springer Verlag; ISBN: 0387503110
- Oda,T. et al. (eds): 1987, Short Wavelength Laser and Their Applications,
Springer Verlag.
- 1986,
Topical Meeting on Short Wavelength Radiation, Generation and Applications : summaries of papers presented at the Short Wavelength Coherent Radiation: Generation and Applications Topical Meeting, March 24-26, 1986, Monterey, California
ISBN: 0936659025
References from
Gasparyan,P.D.,
Starikov,F.A.,
Starostin,A.N.: 1998, Physics - Uspekhi 41 761
Angular divergence and spatial coherence of x-ray laser radiation
- Prokhorov, A.M.: 1965, Science 149 828
- Robinson, C.A. : 1981, Aviation Week and Space Technol. 114 25
- Canavan, G.H., Bloembergen, N., Patel, C.K.N. : 1987, Physics Today 40 (11) 48 "Debate on APS directed-energy weapons study"
- Broad, W.J.: 1992, Teller's War (New York: Simon & Schuster)
- Matthews, D.L. et al.: 1985, Phys. Rev. Lett. 54 110
- Rosen, M.D. et al.: 1985, Phys. Rev. Lett. 54 106
- Suckewer, S. et al.: 1985, Phys. Rev. Lett. 55 1753
- Elton, R.C.: 1975, Appl. Optics 14 97; Zherikhin, A.N., Koshelev. K.N., Letokhov, V.S.: 1976, Kvantovaya Elektron. 3 152 [1976, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 6 82]; Vinogradov, A.V., Sobel'man, I.I., Yukov, E.A.: 1977, Kvantovaya Elektron. 4 63 [1977, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 7 32]
- Gudzenko, L.I., Shelepin, L.A.: 1963, Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 45 1445 [1964, Sov. Phys. JETP 18 998]; Pert, G.J.: 1976, J. Phys. B 9 3301; 1979, 12 2067
- Matthews, D L et al. : 1987, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 4 575
- Keane, C J et al. : 1989, J. Phys. B 22 3343
- London, R A et al. : 1989, J. Phys. B 22 3363
- Skinner, C 1991, Phys. Fluids B 3 2420
- Fill, E E : 1995, in Laser Interaction with Matter (IOP Conf. Ser., Vol. 140, Ed. S J Rose) (Bristol: IOP Publ., ) p.111
- Elton, R C 1990, X-Ray Lasers (Boston: Academic Press)
- X-Ray Lasers: 1990 (IOP Conf. Ser., Vol. 116, Ed. G J Tallents) (Bristol: IOP Publ.)
- X-Ray Lasers: 1992 (IOP Conf. Ser., Vol. 125, Ed. E E Fill) (Bristol: IOP Publ.)
- X-Ray Lasers: 1994 (AIP Conf. Proc., Vol. 332, Eds D C Eder, D L Matthews) (Williamsburg: AIP Publ.)
- X-Ray Lasers: 1996 (IOP Conf. Ser., Vol. 151, Eds S Svanberg, C-G WahlstroÈm) (Bristol: IOP Publ.)
- Nickles, P V et al. : 1995, Proc. SPIE 2520 373
- Afanas'ev Yu V, Shlyaptsev V N.: 1989, Kvantovaya Elektron. 16 2499 [1989, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 19 1606]
- Eder, D C et al. , in Ref. [19] p. 136
- Lemoff, B et al. : 1995, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74 1574
- Rocca, J J et al. : 1994, Phys. Rev. Lett. 73 2192
- Rocca, J J et al. , in Ref. [19] p. 176
- Matthews, D L, in Ref. [19] p. 32
- Applications of X-Ray Lasers (Eds R London, D Matthews, S Suckewer) (San Francisco: Nat. Tech. Inform. Serv. Doc. No. LLNL-CONF-9206170, 1992)
- Koch, J A et al. : 1992, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68 3291
- London, R A 1993, Phys. Fluids B 5 2707
- Vinogradov, A V et al. : 1989, Zerkal'naya Rentgenovskaya Optika (X-Ray Mirror Optics) (Leningrad: Mashinostroenie); Chakraborty, P.: 1991, Int. J. Modern Phys. B 5 2133
- Allen, L, Peters, G I.: 1970, Phys. Lett. A 31 95
- Peters, G I, Allen, L 1971, J. Phys. A 4 238; Allen L, Peters G I 1971, J. Phys. A 4 377; 1971, J. Phys. A 4 564
- Peters, G I, Allen, L 1972, J. Phys. A 5 546
- Michalas, D.: 1978, Stellar Atmospheres (San Francisco: W.H. Freeman and Co.)
- Biberman, L M, Vorob'ev, V S, Yakubov, I T Kinetika Neravnovesno Nizkotemperaturno Plazmy (Kinetics of Nonequilibrium Low-Temperature Plasma) (Moscow: Nauka, 1982) [Translated into English (New York: Consultants Bureau, 1987)]
- Rautian, S G, Smirnov, G N, Shalagin, A M 1979, Nelineinye Rezonansy v Spektrakh Atomov i Molekul (Nonlinear Resonances in Spectra of Atoms and Molecules) (Novosibirsk: Nauka)
- Gasparyan, P D et al. : 1994, Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 105 1593 [1994, JETP 78 858]
- Zemtsov, Yu K, Sechin, A Yu, Starostin, A N 1996, Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 110 1654 [1996, JETP 83 909]
- Maitland, A., Dunn, M.H.: 1969, Laser Physics (Amsterdam: North-Holland Publ. Co.)
- Rytov, S M, Kravtsov, Yu A, Tatarski, V I 1978, Vvedenie v Statistiches-kuyu Radiofiziku Part 2 (Principles of Statistical Radiophysics)(Moscow: Nauka) [Translated into English (Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1989)]
- Apresyan, L A, Kravtsov, Yu A 1983, Teoriya Perenosa Izlucheniya (Theory of Radiation Transfer) (Moscow: Nauka)
- Landau, L D, Lifshitz, E M Elektrodinamika Sploshnykh Sred (Electrodynamics of Continua Media) (Moscow: Nauka, 1981) [Translated into English (New York: Pergamon Press, 1984)]
- Born, M, Wolf, E 1964, Principles of Optics 4th ed. (Oxford, New York: Pergamon Press)
- Gudzenko, L I, Yakovlenko, S I 1978, Plazmennye Lazery (Plasma Lasers) (Moscow: Atomizdat)
- London, R A 1988, Phys. Fluids 31 184
- Boswell, B et al. : 1990, Phys. Fluids B 2 436
- Boehly, T et al. : 1990, Opt. Commun. 79 57
- Ratowsky, R P et al. : 1994, ICF Quart. Rep. UCRL-LR 105821-94-2 (Livermore: LLNL) 4 (2) 63
- Plowes, J A, Pert, G J, Holden, P B 1995, Opt. Commun. 116 260
- Wan, A S, Mayle, R W, Kato, Y, Osterheld, A L,: 1996, in Laser Interaction and Related Plasma Phenomena (AIP Conf. Proc., Vol. 369, Eds S Nakai, G N Miley) (New York: AIP Conf.) part 2, p. 778
- Zimmerman, G B, Kruer, W L 1975, Comments Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 11 51
- Avrorin, E N et al. : 1980, Pis'ma Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 32 457 [1980, JETP Lett. 32 437]
- Craxton, R S, MacCrory, R L 1980, LLE Reports 99 and 108 (Rochester: University of Rochester, )
- Sofronov, I D et al., in Konstruirovanie Algoritmov i Reshenie Zadach Matematichesko Fiziki (Construction of Algorithms and Solution to Problems of Mathematical Physics) (Eds G P Voskresenski, V V Zabrodin) (Moscow: Inst. of Problems in Mechanics, USSR Acad. Sciences, 1989)
- Klisnick, A et al. , in Ref. [17] p. 305
- Klapisch, M et al. : 1977, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 67 148
- Hagelstein, P L 1981, LLNL Report UCRL-53100 (Livermore: LLNL)
- Voinov, B Aet al. : 1993, Vopr. Atom. Nauki Tekhn., Ser. Matem. Model. (2) 65
- Politov, V Yu, Lykov V A, Shinkarev M K 1993, Proc. SPIE 1928 157
- Makhrov, V et al. : 1994, J. Phys. B 27 1899
- Holden, P B et al. : 1994, J. Phys. B 27 341
- Derzhiev, V I et al. : 1987, Preprint IOFAN No. 235 (Moscow: Inst. Gen. Phys. Publ.); Derzhiev V I, Zhidkov A G, Yakovlenko S I 1992 , Trudy IOFAN 40 52
- Limpoukh, � I, Rozanov, V B 1984, Kvantovaya Elektron. 11 1416 [1984, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 14 955]
- Rosen, M D 1990, Phys. Fluids B 2 1461
- Willi, O et al. : 1990, Phys. Fluids B 2 1318
- Kieffer, J C et al. : 1991, Phys. Fluids B 3 463
- Nantel, M et al. : 1993, Phys. Fluids B 5 4465
- La Fontaine, B et al. : 1993, Phys. Rev. E 47 583
- Wan, A S et al. , in Ref. [19] p. 504
- Hora, H 1981, Physics of Laser Driven Plasmas (New York: John Wiley and Sons)
- Pantell, R H, Puthoff, H E 1969, Fundamentals of Quantum Electronics (New York: Plenum Press)
- Allen, L, Eberly, J H 1975, Optical Resonance and Two-Level Atoms (New York: John Wiley and Sons)
- Leontovich M.: 1944, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Fiz. 8 16
- Hopf, F A, Meystre P 1975, Phys. Rev. A 12 2534; Raymer M G, Mostowski J 1981, Phys. Rev. A 24 1980; Raymer M.G. et al. : 1985, Phys. Rev. A 32 332
- Hazak, G, Bar-Shalom, A 1988, Phys. Rev. A 38 1300
- Sureau, A, Holden, P B 1995, Phys. Rev. A 52 3110
- Ratowsky, R P, London, R A 1995, Phys. Rev. A 51 2361
- Hazak, G, Bar-Shalom, A 1989, Phys. Rev. A 40 7055
- London, R A, Strauss, M, Rosen, M D 1990, Phys. Rev. Lett. 65 563
- Amendt, P, London, R A, Strauss, M 1991, Phys. Rev. A 44 7478
- Amendt, P, London, R A, Strauss, M 1993, Phys. Rev. A 47 4348
- Borovski, A V, Galkin, A L, Korobkin, V V 1988, Kvantovaya Elektron. 15 1457 [1988, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 18 915]; Borovski, A V, Galkin A L : 1993, Trudy IOFAN 41 103
- Ladagin, V K, Starikov, F A, Volkov, V A, in Ref. [19] p. 336
- Feit, M D, Fleck, J A, Jr. 1990, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 7 2048
- Feit, M D, Fleck, J A, Jr. 1991, Opt. Lett. 16 76
- Starikov, F A 1989, Vopr. Atom. Nauki Tekhn., Ser. Teor. Prikl. Fiz. (4) 14
- Starikov, F A 1990, Vopr. Atom. Nauki Tekhn., Ser. Teor. Prikl. Fiz. (2) 33
- Starikov, F A, Urlin, V D 1991, Kvantovaya Elektron. 18 436 [1991, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 21 393]
- Akhmanov, S A, D'yakov Yu E, Chirkin A S Vvedenie v Statisti-cheskuyu Radiofiziku i Optiku (Introduction to Statistical Radio-physics and Optics) (Moscow: Nauka, 1981)
- Starikov, F A 1990, Vopr. Atom. Nauki Tekhn., Ser. Teor. Prikl. Fiz. (3) 20
- Starikov, F A 1992, Kvantovaya Elektron. 19 527 [1992, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 22 483]
- Starikov, F A 1995, in Fizika Yaderno-Vozbuzhdaemo Plazmy i Problemy Lazerov s Yaderno Nakachko Vol. 2 (Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Physics of Nuclear-Excited Plasmas and Problems of Nuclear-Pumped Lasers) (Arzamas-16: VNIIEF) p. 260; 1996, Kvantovaya Elektron. 23 205 [1996, Quantum Electron. 26 199]
- Linford, G J et al. : 1974, Appl. Optics 13 379
- Kryuchenkov, V B et al. : 1990, Kvantovaya Elektron. 17 189 [1990, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 20 146]
- Mokhov, Yu V : 1991, Vopr. Atom. Nauki Tekhn., Ser. Teor. Prikl. Fiz. (1) 29
- Starikov, F A 1994, Kvantovaya Elektron. 21 343 [1994, Quantum Electron. 24 320]
- Chirkov, V A 1984, Kvantovaya Elektron. 11 2253 [1984, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 14 1497]
- Bunkin, F V, Bykov, V P 1986, Kvantovaya Elektron. 13 869 [1986, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 16 569]
- Fill, E E 1988, Opt. Commun. 67 441
- Ladagin, V K, Starikov F A, Urlin V D 1993, Kvantovaya Elektron. 20 471 [1993, Quantum Electron. 23 406]
- MacGowan, B J et al. : 1986, Proc. SPIE 688 36
- Whelan, D A et al. : 1987, Proc. SPIE 831 275
- Zhidkov, A G, Terskikh A O, Yakovlenko S I 1988, Kratk. Soobshch. Fiz. (9) 27; Gulov A V et al. : 1990, Kvantovaya Elektron. 17 753 [Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 20 675 (1990)]
- Volkov, V A et al. : 1991, Kvantovaya Elektron. 18 1329 [1991, Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 21 1214]
- Zahavi, O, Hazak, G, Zinamon, Z J. 1993, Opt. Soc. Am. B 10 271
- Trebes, J E et al. : 1992, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68 588
- Lee, T N, McLean, E A, Elton, R C 1987, Phys. Rev. Lett. 59 1185
- O'Neil, D M et al. : 1990, Opt. Commun. 75 406
- Starikov, F A 1993, Kvantovaya Elektron. 20 477 [1993, Quantum Electron. 23 412]
- Starikov, F A, in Ref. [19] p. 315
- Sutton, G W 1969, AIAA Journal 7 1737
- Lutovinov, V S, Chechetkin V R 1987, Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 93 1602 [1987, Sov. Phys. JETP 66 916]
- Amendt, P, Strauss, M, London R 1996, Phys. Rev. A 53 R23
- Suckewer, S et al. : 1986, Phys. Rev. Lett. 57 1004
- Tomasel, F G, Shlyaptsev, V N, Rocca J J 1996, Phys. Rev. A 54 2474
- Nilsen J 1993, Phys. Scr. T47 83
- Boehly, T et al. : 1990, Phys. Rev. A 42 6962
- Nilsen, J et al. : 1993, Phys. Rev. A 48 4682
- Moreno, J C, Nilsen, J, Da Silva, L B 1994, Opt. Commun. 110 585
- Holden, P B, Rus B 1995, Opt. Commun. 119 424
- Li, Y, Pretzler, G, Fill, E E 1995, Phys. Rev. A 51 R4341; 1995, Opt. Commun. 119 557; Li Y, Pretzler G, Fill E E, Nilsen J : 1996, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 13 742
- MacPhee, A G et al. , in Ref. [19] p. 50
- Tallents, G J et al. , in Ref. [19] p. 372
- Plowes, J A, Pert, G J, Holden, P B : 1995, Opt. Commun. 117 189
- Starikov, F A 1997, Kvantovaya Elektron. 24 691 [1997, Quantum Electron. 27 673]
- Jaegle, P et al. , in Ref. [19] p. 1
- Nilsen, J et al. : 1997, Phys. Rev. A 55 827
- Lu, P, Li, Y, Fill, E E : 1996, Phys. Rev. A 54 5193
- Albert, F et al. in Ref. [19] p. 427
- Shlyaptsev, V N et al. in Ref. [19] p. 215
- Bonnet, L, Jacquemot, S, in Ref. [19] p. 53; Schegel Th, Nickles P V, Sandner W, in Ref. [19] p. 91
- Fiedorowicz, H et al. : 1996, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 415
- Fiedorowicz, H et al. , in Ref. [19] p. 76
- Rosen, M D, Trebes, J E, Matthews, D L 1987, Comments Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 10 245
- Shimkaveg, G Met al. , in Ref. [17] p. 61
- Rus, B et al. : 1995, Phys. Rev. A 51 2316
- Ceglio, N M et al. : 1988, Appl. Opt. 27 5022
- Ceglio, N M et al. : 1988, Opt. Lett. 13 108
- Hara, T et al. , in Ref. [19] p. 200
- Da Silva, L B et al. : 1993, Proc. SPIE 2012 158
- Lunney, J G Appl. Phys. Lett. 48 891 (1986)
- Kodama, R et al. : 1994, Phys. Rev. Lett. 73 3215
- Daido, H et al. : 1995, Opt. Lett. 20 61
- Yuan, G et al. : 1995, Phys. Rev. A 52 4861
- Plowes, J A, Pert, G J, Holden, P B 1995, Opt. Commun. 116 260
- Nilsen, J et al. : 1996, Opt. Commun. 124 287; 1996, 130 415
- Hagelstein, P L 1983, Plasma Phys. 25 1345
- Lewis, C L S et al. : 1992, Opt. Commun. 91 71
- Wang, S et al. : 1992, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 9 360
- Carillon, A et al. : 1992, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68 2917
- Key, M H et al. , in Ref. [19] p. 9
- Shvarts, D et al. : 1987, Proc. SPIE 831 283
- Boehly, T et al. : 1987, Proc. SPIE 831 305
- Boehly, T et al. : 1990, Appl. Phys. B 50 165
- Pert G, J et al. , in Ref. [19] p. 260
 X-RAY LASER
X-RAY LASER X-RAY LASER
X-RAY LASER PRACTICAL USES OF X-RAY LASERS
PRACTICAL USES OF X-RAY LASERS