Laser Discovered in BN star
The possibility of laser action in astrophysical sources was considered
by Smith
(1969), Menzel (1970) and later demonstrated
by Varshni (1973, 1979).
Smith
et al. (1979) discovered that the Becklin-Neugebauer (BN) star
in the Orion nebula also emitted laser radiation.
Its spectra was observed in the range of 3.3 to 5.5 microns. Atomic hydrogen
emission lines of Brackett-alpha and Pfund-beta were seen, as well as molecular
CO absorptions. The December 1976 data showed an anomalously high intensity
for Pfund-beta line near 4.65 microns. Theoretical considerations suggested
that Pfund-beta radiation arises in a small dense region, with the transition
possibly lasing. It is not surprising that microwave
lasers have also been found in this area (crosses marked on chart below).
Smith has observed the Pfund beta intensity anomaly in
gamma Cas and zeta Tau, both Be
shell stars.
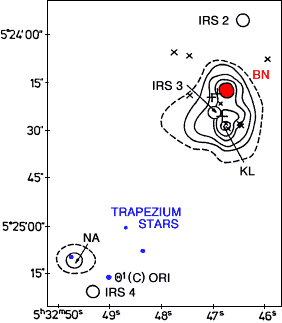 20 micron infrared image of area near the BN star (in red).
This star is a member of the stellar association of young
stars in the orion nebula which includes the Trapezium
cluster (in blue). The crosses give the
positions of OH and H2O masers (hydroxyl
and water masers). The image has a resolution of 5 arcseconds. (By
permission of Wynn-Williams and Becklin, 1974)
20 micron infrared image of area near the BN star (in red).
This star is a member of the stellar association of young
stars in the orion nebula which includes the Trapezium
cluster (in blue). The crosses give the
positions of OH and H2O masers (hydroxyl
and water masers). The image has a resolution of 5 arcseconds. (By
permission of Wynn-Williams and Becklin, 1974)
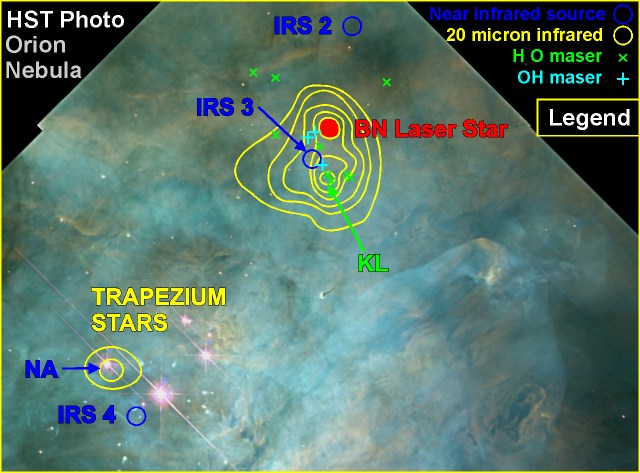
Hubble Space Telescope optical image of Trapezium
cluster in the Orion nebula overlayed with infrared contour lines (in
yellow) from previous plot. The laser star is prominent in the recent infrared
image from the HST
(it is the brightest object in the NICMOS image which covers 0.8
to 2.5 microns of wavelength)
This is an area of active star formation; just below center of the image
there is an extended 'comet
like' object indicating strong stellar winds. In higher resolution
images there are a dozen
of these objects oriented radially around Theta1 Orionis (the brightest
of the Trapezium stars in this image).
 Closeup of BN star at wavelength of 3.8 microns. Field of view is 20 arcseconds across.
(Dougados et al., 1993)
Closeup of BN star at wavelength of 3.8 microns. Field of view is 20 arcseconds across.
(Dougados et al., 1993)
 Infrared spectrum of BN star taken in December 1976. Covers 4.45 to 4.75 microns.
The Pfund beta hydrogen laser emission line is prominent at 4.65 microns.
(Smith et al., 1979)
Infrared spectrum of BN star taken in December 1976. Covers 4.45 to 4.75 microns.
The Pfund beta hydrogen laser emission line is prominent at 4.65 microns.
(Smith et al., 1979)
REFERENCES
-
Smith,H.A.:
1969, ApJ., 158, 371. Possibility of laser action in
astrophysical sources
-
Smith,H.A.,
Larson,H.P., Fink,U.: 1979, ApJ., 233, 132. The spectrum
of the Becklin-Neugebauer source in Orion from 3.3 to 5.5 microns
-
Hall,D.N.B.,
Ridgway,S.T., Gillett,F.C., Kleinmann,S.G.: 1978, ApJ., 223,
47. High-resolution 1.5-5 micron spectroscopy of the Becklin-Neugebauer
source in Orion
-
Scoville,N.Z.,
Hall,D.N.B., Ridgway,S.T., Kleinmann,S.G.: 1982, NASA, NSF, New York Academy
of Sciences, et al., Symposium on the Orion Nebula to Honor Henry Draper,
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 395, p. 125.
Gas dynamics in the circumstellar Nebula on the Becklin-Neugebauer source
-
Scoville,N.,
Kleinmann,S.G., Hall,D.N.B., Ridgway,S.T.: 1983, ApJ., 275,
201. The circumstellar and nebular environment of the Becklin-Neugebauer
object - 2-5 micron wavelength spectroscopy
-
Dougados,C.,
Lena,P., Ridgway,S.T., Christou,J.C., Probst,R.G.: 1993, ApJ., 406,
112. (online) Near-infrared imaging of the Becklin-Neugebauer-IRc2
region in Orion with subarcsecond resolution
-
Scoville,N.Z.,
Hall,D.N.B., Ridgway,S.T., Kleinmann,S.G.: 1979, ApJ., 232,
121. Detection of CO band emission in the Becklin-Neugebauer object
Laser History

 20 micron infrared image of area near the BN star (in red).
This star is a member of the stellar association of young
stars in the orion nebula which includes the Trapezium
cluster (in blue). The crosses give the
positions of OH and H2O masers (hydroxyl
and water masers). The image has a resolution of 5 arcseconds. (By
permission of Wynn-Williams and Becklin, 1974)
20 micron infrared image of area near the BN star (in red).
This star is a member of the stellar association of young
stars in the orion nebula which includes the Trapezium
cluster (in blue). The crosses give the
positions of OH and H2O masers (hydroxyl
and water masers). The image has a resolution of 5 arcseconds. (By
permission of Wynn-Williams and Becklin, 1974)
 Closeup of BN star at wavelength of 3.8 microns. Field of view is 20 arcseconds across.
(
Closeup of BN star at wavelength of 3.8 microns. Field of view is 20 arcseconds across.
( Infrared spectrum of BN star taken in December 1976. Covers 4.45 to 4.75 microns.
The Pfund beta hydrogen laser emission line is prominent at 4.65 microns.
(
Infrared spectrum of BN star taken in December 1976. Covers 4.45 to 4.75 microns.
The Pfund beta hydrogen laser emission line is prominent at 4.65 microns.
(