 |
ALL aircraft. From Boeing NKC-135 Airborne Laser Lab-ALL - USAF Museum Airpark
- Manufacturer : Boeing
- Specifications :
- Span: 39.88 m
- Length: 41.53 m
- Height: 12.70 m
- Weight: 136,000 kg loaded
- Armament: None
- Engines: Four Pratt & Whitney J-57 turbojet engines of
61,160 Newton thrust each with water injection
- Electrical Generators :
- Type : Same as on B-52G aircraft
- Number : 3
- Power : 280 kVA
- Rotation speed : independent of engine speed
- Crew: Four (plus 80 troops)
- Cost: $3,398,000 U.S.
- Serial number: 55-3123
- Performance
- Maximum Speed: 975 km/h
- Cruising Speed: 824 km/h
- Service Ceiling: 15,240 m
- Range: 13,960 km
- Structure :
- Pressure bulkheads :
- location : one at front between cockpit and laser module and another between laser module and rear control room.
- purpose : laser compartment is pressurize 4 percent lower than other compartments to prevent toxic gases from entering crew compartments.
The bulkheads also act as firewalls.
- material : aluminum covered with 0.81 mm stainless-steel layer.
- Blowout doors : strategically placed to re-direct overpressure from accidental explosion.
- Emergency Laser Fuel Dump : in less than 5 minutes
- diagnostics :
- 4 color video cameras with zoom lenses monitor laser and exhaust plume of gas dynamic laser.
- IR gas analysis detection system monitors gas leaks
|
|
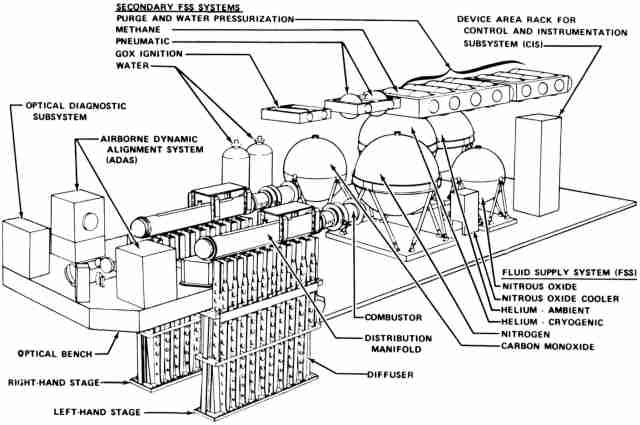 |
Gas Dynamic Laser
- Photo Source : Duffner, R.W.L : 1997, Airborne Laser, Bullets of Light, ISBN 0-306-45622-2 Plenum Press, New York
- Photo Credit : Phillips Laboratory Archives
- composition of lasant : CO2 - N2 - H2O
- number : 2 stages
- raw power : 0.456 MW before passing through ADASS/APT (1979)
- power : 0.38 MW immediately after beam exits aircraft (1979)
- effective power : approximately 10 percent of power on target at 1 km range (1979)
- effective power flux : > 102 W cm-2 at 1 km range (damage threshold for guidance systems of most heat seeking missiles)
- efficiency : 4 %
- manufacturer : Pratt & Whitney
- cost : $ 32.1 million U.S.
- date : 1976
- beam duration : 7.9 sec maximum
- maintenance :
- dust :
- problem 1 : when dust is placed in the path of a high energy laser beam the side of the particle exposed to the beam
vaporizes, imparting momentum to the particle, like a miniature rocket engine. The accelerated particle
may disintegrate or it may collide at high speeds with sensitive optical components.
- solution : clean room air quality required
- problem 2 : if the beam ignites the particle this causes a sparkle effect that may interfere with beam sensors
- solution 2a : make beam sensors less sensitive to the spectrum of the exploding dust
- solution 2b : make beam sensors more sensitive to the laser radiation by using a narrow band filter
- Combustor
- location : short pipe just before distribution manifold
- purpose : furnace where components are mixed and burned before being fed to distribution manifold
- manufacturer : Rocketdyne, Canoga Park, California.
- cost : $ 1.9 million U.S.
- maintenance : burning gases leave deposits in combustor injectors
- Gas composition/sequencing
- When first started :
- composition : CH4 and O2 (start-up reactants)
- procedure : Spark plug ignites the gases
- purpose : provide a uniform high temperature flame front in both combustors in preparation for main reactant injection.
- After a few seconds :
- composition : CO and N2O (main reactants)
- procedure : main reactants are injected into uniform flame front and combust.
- purpose : provide highly excited N2 and CO2 molecules at a high temperature before expansion in nozzles
- additives :
- composition : some CH4 and O2
- purpose : provide traces of H2O essential for efficient laser action
- Downstream :
- additives :
- material : N2
- location : fed into secondary injectors in downstream chamber
- purpose : diluent
- After thorough combustion and mixing :
- composition : CO2 (14 %), N2 (85 %), H20 (1 %)
- pressure : 55 atmospheres
- temperature : 1900 deg K
- Distribution manifold
- dimension :
- purpose : provide homogeneous source of hot gases to nozzle array to increase laser beam quality
- safety : a thermal heat shield insulates the chamber
- Nozzles
- dimension : 100 x 12 mm and 0.165 mm throat
- material : nickel plated titanium
- number : 170
- cooling system : liquid N2 flows through two pipes inside each nozzle ridge
- flow velocity : Mach 6 at nozzle exit (hypersonic)
- Resonator
- location : adjacent to nozzle exit
- type : unstable resonator configuration (one convex cavity mirror and one concave cavity mirror)
- dimension : 0.11 x 0.30 x 2.1 m
- pressure : 0.1 atmospheres
- number of passes : 3
- stage coupling : inter-stage beam duct allows beam to pass through both stages
- output : beam exits right stage via aerodynamic window
- Aerodynamic window
- purpose : to extract the final beam from the resonator chamber without using easily damaged glass windows
- geometry : physical opening in resonator chamber
- seal :
- material : thin sheet of nitrogen gas is flowed over the opening
- purpose : prevent outside air at higher pressure from entering the lower pressure resonator chamber
- control : variable supply of nitrogen gas to the control valve regulator to compensate for different resonator pressures
- Diffuser
- manufacturer : Pratt & Whitney
- maintenance : burning gases leave deposits on diffuser wall ejectors
- Exhaust
- location : just after diffuser
- dimension : 2.1 x 0.46 m
- thrust : 18,000 Newton when operating (about one third the force of one
jet engine)
- temperature : 870 deg K (gas)
- pressure : near one atmosphere
- Exhaust duct
- location : just below diffuser
- material : lined with corrugated titanium 2.3 mm thick
- purpose : heat resistance
- Exhaust port doors
- location : bottom of aircraft just forward of the wing root
- purpose : to reduce drag on aircraft when laser is not
operating and to protect laser
- material : aluminum with silicon rubber layer over inner skin for thermal insulation
- powered by : hydraulic fluids
- opening time : 1 sec
- closing time : 5 sec
- comment : resembles mini bomb bay doors
- Exhaust door spoiler :
- location : outside aircraft just ahead of exhaust port doors
- material : 6.4 mm thick steel plate perforated with 505 holes 9.5 mm in diameter
- purpose : break up the airflow to :
- minimize hot exhaust gases from hitting side of aircraft
- allow doors to open and close efficiently
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
|





